Date/Time Parser Code Generator
Generate parsing code for any date/time format in JavaScript, Python, Java, PHP, and more.
Input Configuration
Generated Code
Free Date/Time Parser Code Generator: Stop Wrestling With Date Formats
Why Date Parsing Is Such a Pain
Let me guess – you’ve got a date string like “12/06/2024 2:30 PM” and you need to parse it in your code. Simple, right?
Wrong. Thirty minutes later you’re still Googling things like “python parse date with AM PM” or “java simpledateformat patterns” and wondering why something so basic has to be this annoying.
Here’s the problem: every programming language handles dates differently. Python uses %Y-%m-%d. Java uses yyyy-MM-dd. PHP uses Y-m-d. JavaScript just kind of wings it and hopes for the best.
And don’t even get me started on:
- Is it MM/DD or DD/MM?
- What’s the format code for month names again?
- How do I handle 12-hour vs 24-hour time?
- Wait, does this support milliseconds?
- Why is my date off by one day? (timezone fun!)
This stuff shouldn’t be hard, but it is. That’s what this tool fixes.
What This Tool Actually Does
The Date/Time Parser Code Generator is dead simple:
- You paste in an example date string (like “2024-12-06 14:30:45”)
- You pick or enter the format pattern
- You choose your programming language
- It spits out working code that parses that exact format
No more hunting through documentation. No more trial and error. Just copy the code and move on with your life.
Pro tip: The tool includes validation code, error handling, and examples of formatting the parsed date back to different formats. It’s not just a one-liner – it’s production-ready code.
Key Features That Matter
Live Preview
Type in your date string and immediately see if it’s valid. No need to run the code to find out you got the format wrong.
Multiple Language Support
Generates code for JavaScript, Python, Java, PHP, C#, and Ruby. Same format, different syntax – all handled automatically.
Preset Common Formats
Click to select from common patterns like ISO 8601, US format (MM/DD/YYYY), European format (DD.MM.YYYY), or Unix timestamps. Don’t reinvent the wheel.
Custom Format Builder
Got a weird format? Build your own using standard tokens (YYYY, MM, DD, HH, mm, ss, etc). The tool converts it to whatever language you need.
Quick Examples
One-click to load common date examples and see how they parse. Great for testing or when you’re not sure what format you’re dealing with.
Copy and Go
One button click copies the entire code block. Paste it into your project and you’re done.
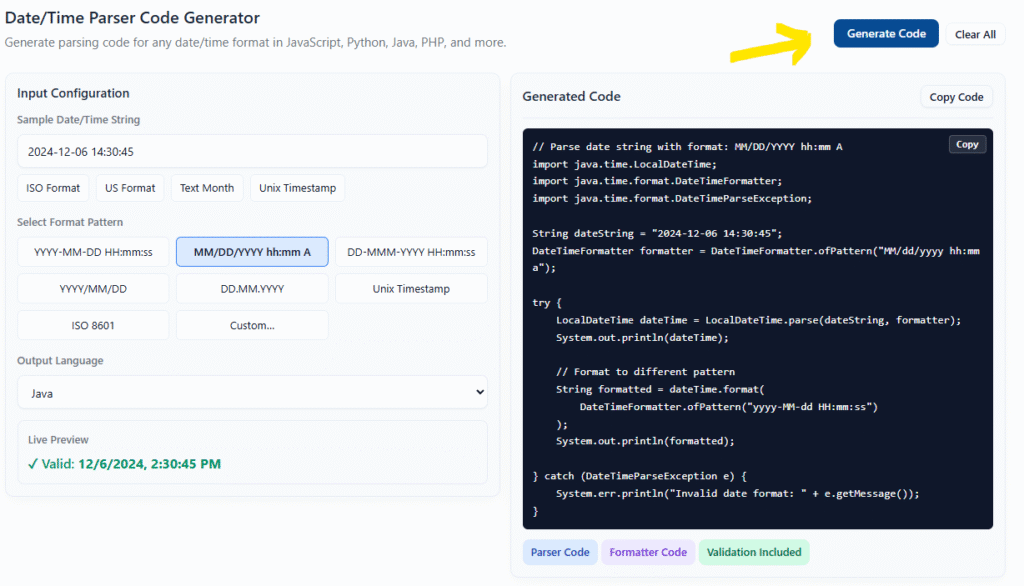
How to Use It (2 Minutes)
Step 1: Enter Your Date String
Paste an example of the date format you’re working with. For example: 06-Dec-2024 14:30:45
Or click one of the quick example buttons to load a common format.
Step 2: Pick Your Format
Select from the preset format patterns or choose “Custom” to build your own. The live preview will tell you if it’s working.
Step 3: Choose Your Language
Select the programming language from the dropdown. The code updates automatically.
Step 4: Copy and Use
Hit “Generate Code”, then click “Copy Code”. Paste it into your project. Done.
That’s it. Seriously. No account needed, no configuration, no installation. Just copy working code and move on.
Supported Languages
JavaScript
Uses native Date object with proper validation. Includes suggestions for popular libraries like date-fns, moment.js, and dayjs when you need more complex parsing.
Python
Uses datetime.strptime with the correct format codes. Includes error handling and examples of formatting the output.
Java
Uses the modern java.time API (DateTimeFormatter and LocalDateTime). No more SimpleDateFormat headaches.
PHP
Uses DateTime::createFromFormat with proper error checking. Shows you how to validate and reformat.
C#
Uses DateTime.ParseExact with InvariantCulture. Includes try-catch for proper error handling.
Ruby
Uses DateTime.strptime with error handling and validation examples.
Common Format Patterns
Here are the most common date/time formats you’ll encounter:
ISO 8601 (Standard)
2024-12-06T14:30:45Z
The international standard. Unambiguous and sortable. Use this when you can.
US Format
12/06/2024 2:30 PM
Month first, 12-hour clock. Common in American systems.
European Format
06.12.2024 14:30
Day first, 24-hour clock. Common in Europe.
Text Month
06-Dec-2024 14:30:45
Uses abbreviated month names. More readable but language-dependent.
Unix Timestamp
1733493045
Seconds since January 1, 1970. Good for storing dates, not for displaying them.
Database Format
2024-12-06 14:30:45
What you get from most SQL databases. Similar to ISO but without the T separator.
Real-World Examples
Parsing API Response Dates
You’re calling an API that returns dates like “2024-12-06T14:30:45.123Z”. You need to display this as “Dec 6, 2024 at 2:30 PM”.
Solution: Select ISO8601 format, choose your language, and you get code that parses the ISO date and shows you how to format it for display.
Reading CSV Files
You’ve got a CSV export with dates in US format: “12/06/2024 2:30 PM”. You need to parse these into proper date objects for processing.
Solution: Enter the example, select MM/DD/YYYY hh:mm A format, and get code with error handling for each row.
Converting Between Formats
Your database stores dates as timestamps, but your frontend needs “Dec 6, 2024” format.
Solution: Use the timestamp format option to see how to convert in both directions with proper validation.
Handling User Input
Users can enter dates in various formats. You need to standardize them.
Solution: Generate parsers for all the formats you want to accept, then normalize to one internal format.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do I need to install anything?
A: Nope. It’s a web tool that runs entirely in your browser. Just open it and use it.
Q: Does it handle timezones?
A: The generated code uses the default timezone behavior for each language. For complex timezone handling, you’ll need additional libraries (which the tool suggests in comments).
Q: What if my format is really weird?
A: Use the custom format option. You can build any pattern using standard tokens (YYYY for 4-digit year, MM for 2-digit month, etc). The tool shows you which tokens are available.
Q: Is the generated code production-ready?
A: Yes, it includes error handling and validation. That said, always test with your actual data – date parsing can have edge cases depending on your specific requirements.
Q: Why not just use a library?
A: You can! For complex cases, libraries like date-fns (JavaScript), dateutil (Python), or Joda-Time (Java) are great. This tool is for when you need something quick without adding dependencies, or when you’re not sure which library to use.
Q: Does it work offline?
A: Yes! Once the page loads, everything runs locally in your browser. No internet required.
Q: Can I parse dates with month names in different languages?
A: The tool generates code for English month names. For other languages, you’ll need locale-specific parsing, which the generated code comments point you toward.
Q: What about milliseconds or microseconds?
A: The standard formats include seconds. For milliseconds, use the custom format option with tokens like SSS (milliseconds). The exact token depends on your target language.
Q: Why does my JavaScript date parsing act weird sometimes?
A: JavaScript’s Date constructor is notoriously inconsistent across browsers and formats. For anything beyond ISO 8601, use a library like date-fns or explicitly parse the components yourself (which this tool helps you do).
Q: Can I modify the generated code?
A: Absolutely. It’s your code. The tool gives you a solid starting point, but feel free to adapt it to your needs.
Q: What if I need to parse multiple different formats?
A: Generate code for each format, then combine them with try-catch blocks to attempt parsing with each format until one succeeds.
Q: Does it handle dates before 1970 or after 2038?
A: For most languages, yes. The tool uses modern date APIs that handle a wide range. Unix timestamps have limitations (especially 32-bit systems and the year 2038 problem), which is why the tool generates proper date object code when possible.
Q: Is my date string private?
A: Yes. Everything happens in your browser. Nothing is sent to any server. Your dates never leave your computer.
Q: Can I use this for commercial projects?
A: Yes. The tool is free to use for any purpose, including commercial projects. The generated code is yours to use however you want.
Tips for Working With Dates
Always Validate
Just because a string matches a format doesn’t mean it’s a valid date. February 31st matches the format but doesn’t exist. The generated code includes validation checks.
Be Explicit About Formats
Don’t rely on automatic parsing if you can avoid it. Explicit format strings make your code clearer and prevent bugs.
Store Dates Consistently
Pick one format for storage (ISO 8601 or Unix timestamps are good choices) and stick to it. Only convert to other formats for display.
Test Edge Cases
Test with dates at the beginning and end of months, years, and centuries. Leap years. Daylight saving time transitions. These are where bugs hide.
Consider Using Libraries
For complex date math or timezone handling, don’t reinvent the wheel. Libraries exist for a reason. This tool is great for simple parsing, but date-fns, Joda-Time, or similar libraries are worth it for heavy date work.
Warning: Never trust user input. Always validate dates, even if they look correct. A malformed date string can crash your app or worse.
When NOT to Use This Tool
Be honest with yourself about what you need:
- Complex timezone handling: If you’re dealing with multiple timezones and need precise conversions, use a dedicated timezone library.
- Date arithmetic: If you need to add/subtract days, calculate differences, or handle business days, use a date library with these features.
- Recurring patterns: If you’re working with recurring events or schedules, you need specialized tools.
- Historical dates: If you’re working with dates before the Gregorian calendar or need to account for calendar changes, this tool won’t help.
- High-precision timing: If you need nanosecond precision or monotonic clocks, use language-specific timing APIs.
For everything else? This tool will save you time.
The Bottom Line
Date parsing shouldn’t take more than a minute of your time. You’ve got actual work to do.
This tool generates the code you need, in the language you’re using, with proper error handling. It’s fast, it’s free, and it works offline.
Stop Googling format strings. Stop debugging why your dates are off by a day. Just generate the code and move on.
Ready to try it? The tool is loaded and waiting. Paste in a date string and see what it can do.
